![]()
TRPV6, a member of one of seven subfamilies of TRP channels, is a non-voltage-gated, non-receptor-operated calcium-specific ion channel. In a healthy state, it plays an important role in calcium absorption from the gut. In an unhealthy state, TRPV6 plays a key role in cancer pathogenesis including cancer cell growth, proliferation, metastasis and resistance to programmed death.
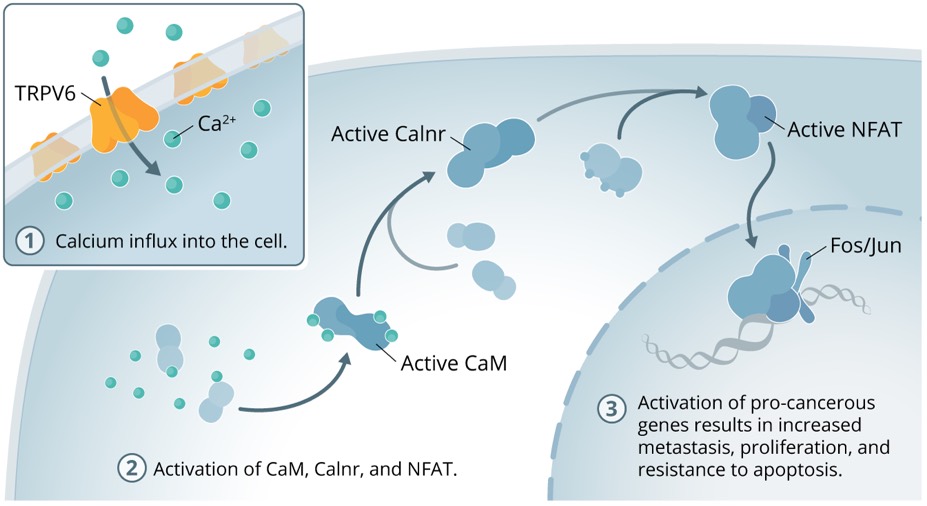
Although the precise details of the TRPV6 pathway in cancer remain to be fully elucidated, a viable model now exists and is based on increased intracellular calcium resulting from the over-expression of TRPV6.
Bolanz, K.A., M.A. Hediger, and C.P. Landowski. Mol Cancer Ther, 2008. 7(2): p. 271-9.
Lehen'kyi, V., et al. Oncogene, 2007. 26(52): p. 7380-5
An increase in TRPV6 expression in the membrane of normal cells activates precancerous pathways by facilitating calcium influx into the cell (1). These calcium ions bind to the calcium binding protein calmodulin (CaM). This complex activates calcineurin (Calnr): a CaM/Ca2+ activated phosphatase that de-phosphorylates and activates Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells (NFAT), a gene transcription factor (2). Active NFAT moves to the nucleus of the cell where, with Jun/Fos (two auxiliary transcription proteins from “cancer causing genes”), activates a number of intracellular pro-cancerous agents (3) including:
Based on the key role that TRPV6 plays in the activation of this pro-cancerous pathway, any inhibition of this calcium channel would be expected to profoundly reduce the cancer cell’s ability to grow, proliferate, metastasize and would make the cell less resistant to apoptotic mechanisms. Over expression of TRPV6 might also be a protective mechanism deployed by cancer cells to avoid apoptotic cell death. Learn how Soricimed is developing new cancer treatments that target and inhibit TRPV6.
Address
18 Botsford St., Suite 201
Moncton, N.B. E1C 4W7
Canada
T: 506.856.0400
F: 506.856.0414
E: info@soricimed.com
© Copyright 2025 Soricimed Biopharma